Ultrasound Specialist
- Home
- Ultrasound Specialist

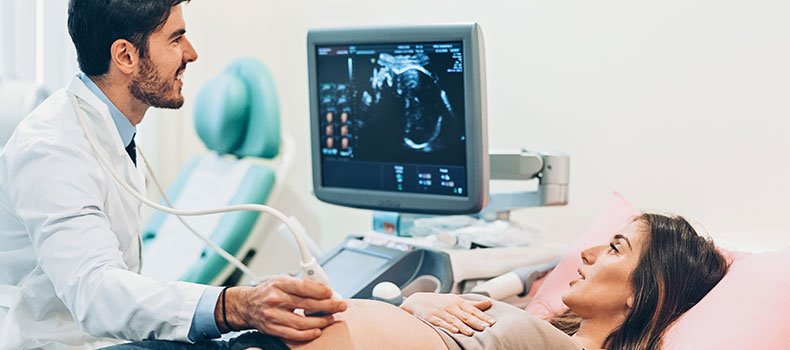
An Ultrasound Specialist, also known as a Sonographer or Diagnostic Medical Sonographer, is a trained healthcare professional who uses ultrasound technology to create images of the inside of the body. These images, known as sonograms, are used to assist doctors in diagnosing and treating medical conditions. Ultrasound specialists play a crucial role in various medical fields, including obstetrics, cardiology, musculoskeletal medicine, and emergency care.
Performing Ultrasound Procedures Ultrasound specialists are responsible for conducting various types of ultrasound exams. These may include:
Preparing and Positioning Patients Ultrasound specialists must prepare the patient for the procedure, ensuring they are in the correct position for clear imaging. For certain ultrasounds, a special gel is applied to the skin to help the sound waves travel more effectively through the body. They explain the procedure to the patient and answer any questions they may have to ensure comfort.
Operating Ultrasound Equipment A key responsibility of the ultrasound specialist is to operate specialized ultrasound machines. These machines use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. The specialist adjusts the settings on the equipment to capture the most accurate and detailed images based on the area of the body being examined.
Interpreting and Analyzing Images Although the ultrasound specialist does not diagnose conditions directly, they play a critical role in capturing high-quality images for the physician. They must have an understanding of normal and abnormal anatomy to ensure that the images are clear and accurate. The specialist may identify areas of concern that will require further investigation by the doctor.
Maintaining Patient Records Ultrasound specialists are responsible for accurately documenting the results of the ultrasound, ensuring that all images and patient information are properly recorded and stored in the medical system for the physician’s review.
Ensuring Patient Safety and Comfort Safety is a priority for ultrasound specialists. They ensure that the ultrasound procedure is performed safely and minimize any discomfort. They also adhere to health and safety protocols for infection control, especially when using ultrasound equipment in different clinical settings.
Diagnostic Ultrasound
Used to examine organs and tissues, such as the heart, kidneys, liver, and reproductive organs, helping to diagnose a range of conditions including tumors, cysts, and infections.
Therapeutic Ultrasound
In some cases, ultrasound is used for therapeutic purposes, such as promoting tissue healing, especially in physical therapy for musculoskeletal conditions.
Obstetric Ultrasound
Specially used during pregnancy to monitor fetal development, detect abnormalities, and check for complications like ectopic pregnancies or placenta issues.
Echocardiography (Cardiac Ultrasound)
Used to examine the heart, evaluate heart valve conditions, blood flow, and detect conditions such as heart disease or congenital heart defects.
Vascular Ultrasound
Focuses on examining blood vessels, detecting blockages, clots, and other vascular problems.
Technical Proficiency
An ultrasound specialist must have a strong understanding of how ultrasound equipment works and be able to operate it efficiently to capture clear, detailed images.
Anatomical Knowledge
A thorough understanding of human anatomy is necessary for recognizing both normal and abnormal findings on ultrasound images. This includes knowledge of the organs, tissues, and structures within the body.
Attention to Detail
Sonographers must pay close attention to detail when capturing images, ensuring that no abnormalities are overlooked. They also need to ensure that the images are of high quality and useful for the doctor’s diagnosis.
Communication Skills
Clear communication is essential when interacting with patients and other healthcare professionals. Ultrasound specialists explain the procedure to the patient, address concerns, and provide clear reports to the physicians.
Physical Stamina
Since ultrasound specialists often need to work long hours or stand for extended periods, physical stamina and the ability to manage the demands of the job are important.
To become an ultrasound specialist, one typically needs the following:
Education
A degree in diagnostic medical sonography is required, which usually includes both classroom instruction and clinical practice. Many sonography programs take about 2 to 4 years to complete, resulting in either an associate’s or bachelor’s degree.
Certification
Certification is often required by employers and is available through various professional organizations, such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) in the United States. Certification may be specific to certain specialties (e.g., obstetrics, cardiac, or musculoskeletal ultrasound).
Licensing
Some regions or countries require ultrasound specialists to hold a state or regional license in addition to certification, particularly in settings where diagnostic testing is done as part of a medical practice.
Ultrasound specialists play a critical role in modern healthcare by using ultrasound technology to help diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. Their expertise in capturing high-quality images of the body’s internal structures aids physicians in diagnosing a wide range of issues, from pregnancy and heart conditions to abdominal and musculoskeletal problems. Their ability to operate specialized equipment, interpret images, and provide high-level patient care is essential to accurate medical diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
WhatsApp us